CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 30, No 1, January/February 2019
AFRICA
37
stress compared to whites, contributed to elevation of BP through
increased TPR and HR.
28
The positive association between 24-hour
HR and renin level may indicate
β
-adrenergic receptor stimulation
at both the heart and kidney, resulting in increases in HR and renin
secretion at the juxtaglomerular apparatus, respectively.
29
Previous
findings in the same population under study indicated that even
at suppressed renin levels, sympathetic stimulation by exposure to
an acute stressor resulted in a positive association between TPR
reactivity and renin reactivity in blacks, but not in whites.
30
The observed association of aldosterone and ARR with
attenuated HR dipping may not only be an indication of possible
synergy between aldosterone and sympathetic drive, but also
the direct effects of aldosterone on the cardiovascular system
via high-density mineralocorticoid receptors.
31,32
The increased
aldosterone sensitivity in blacks
13
may also explain the observed
negative association with HR dipping, despite having lower
mean aldosterone levels compared to whites.
In the present study we also found blacks to have lower
noradrenaline levels, which showed a borderline significant
relationship with aldosterone. Experimental studies indicated
that aldosterone prevents extraneuronal and myocardial uptake
of noradrenaline and therefore may enhance its effects,
15,33
albeit
at lower levels.
The higher frequency of low renin and aldosterone levels in
blacks compared to whites is consistent with previous studies.
34,35
However, blacks exhibited a higher ARR. A relatively higher
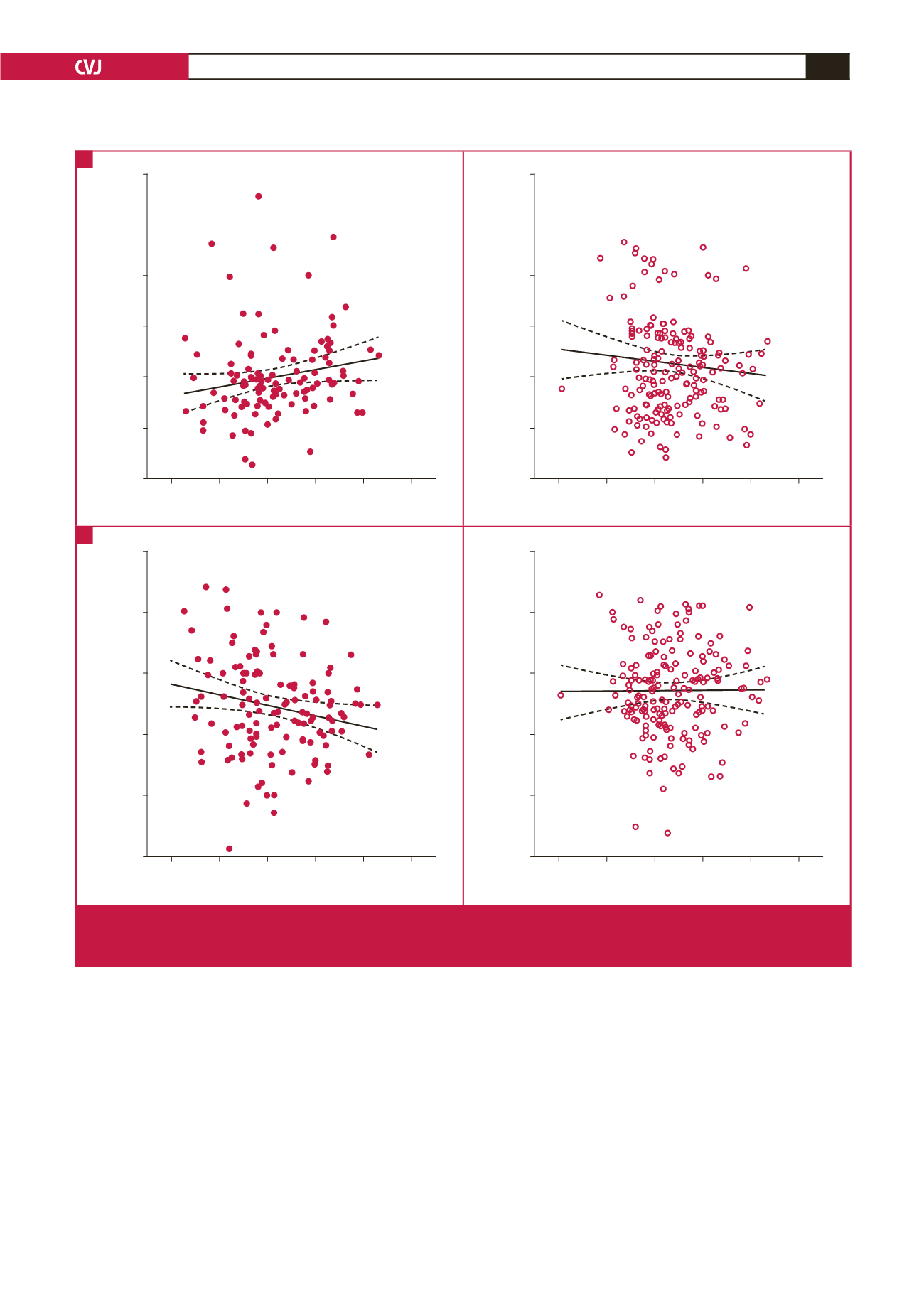
Log aldosterone (pg/ml)
0.8
1.2
1.6
2.0
2.4
2.8
Nordadrenaline:creatinine ration
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
r
=
0.23;
p
=
0.017
Black
Log aldosterone (pg/ml)
0.8
1.2
1.6
2.0
2.4
2.8
Nordadrenaline:creatinine ration
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
r
=
–0.07;
p
=
0.37
White
Log aldosterone (pg/ml)
0.8
1.2
1.6
2.0
2.4
2.8
% Dipping heart rate
40
30
20
10
0
–10
r
=
–0.19;
p
=
0.038
Log aldosterone (pg/ml)
0.8
1.2
1.6
2.0
2.4
2.8
% Dipping heart rate
40
30
20
10
0
–10
r
=
0.008;
p
=
0.92
Fig. 1.
Associations between (A) log noradrenaline:creatinine ratio and log aldosterone; (B) night-time dipping in heart rate and
aldosterone level in black and white groups. Solid and dashed lines represent the regression line and 95% CI boundaries,
respectively.
A
B