CARDIOVASCULAR JOURNAL OF AFRICA • Volume 30, No 1, January/February 2019
38
AFRICA
aldosterone level for a given level of plasma renin points
to the possibility of excess aldosterone secretion, which has
a significant role in salt/volume-related hypertension.
36-38
Higher ARR has been linked to a non-dipping pattern of BP
in the presence of high dietary sodium levels in the general
Japanese population.
39
In our study, we showed that aldosterone and its ratio to
renin were associated with an increase in BP dipping and
a decrease in HR dipping. The favourable association of
aldosterone and ARR with BP dipping may possibly be as a
result of a compensatory mechanism for the reduced dipping
in HR to maintain haemodynamic balance.
Our study should be interpreted within the context of
its strengths and limitations. We did not collect 24-hour
urine in order to assess noradrenaline level, and we did not
assess salt intake, salt sensitivity or angiotensin II levels.
Even though the use of catecholamines is not regarded as
the gold standard, catecholamines and their metabolites are
still used to assess sympathetic activity
24
and therefore the
noradrenaline:creatinine ratio was used in our study. This
was a cross-sectional study therefore causality could not be
inferred. This homogenous sample cannot be regarded as
representative of the general South African population.
Conclusion
We found in blacks only that aldosterone level and its ratio
to renin was associated with less dipping in night-time HR.
Our findings suggest that low-renin hypertension in black
populations may be partly mediated by the direct effects of
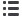
Table 3. Pearson and partial correlations of percentage dipping in night-time
BP and HR with renin, aldosterone and ARR in black and white groups
Pearson correlations
Blacks (
n
=
127)
% SBP
% DBP
% HR
Variables
r
p
r
p
r
p
Log renin
0.05 0.59 0.03 0.72 0.13 0.14
Log aldosterone
0.23 0.010 0.28 0.002 –0.19 0.038
Log ARR
0.16 0.065
0.22 0.013 –0.25 0.004
Whites (
n
=
179)
% SBP
% DBP
% HR
r
p
r
p
r
p
Log renin
0.13 0.091
0.19 0.009
0.12 0.11
Log aldosterone
0.07 0.39 0.09 0.22 0.001 0.92
Log ARR
–0.03 0.64 –0.06 0.42 –0.08 0.26
Adjusted for age, gender
and BMI
Blacks (
n
=
127)
% SBP
% DBP
% HR
r
p
r
p
r
p
Log renin
0.06 0.51 0.05 0.61 0.11 0.24
Log aldosterone
0.26 0.004 0.31
<
0.001 –0.19 0.025
Log ARR
0.19 0.23
0.24 0.008 –0.25 0.006
Whites (
n
=
179)
% SBP
% DBP
% HR
r
p
r
p
r
p
Log renin
0.14 0.062
–0.17 0.021
0.10 0.19
Log aldosterone
0.08 0.28 0.09 0.24 0.001 0.99
Log ARR
–0.03 0.72 –0.05 0.55 –0.07 0.34
SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure, HR, heart rate; ARR,
aldosterone-to-renin ratio; BMI, body mass index. Bold text indicates
p
<
0.05.
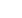
Table 2. Pearson and partial correlations of BP, HR and noradrenaline
with renin, aldosterone and ARR in black and white groups
Pearson
correlations
Blacks (
n
=
127)
24-hour SBP 24-hour DBP 24-hour HR
NA:creatinine
ratio
Variables
r
p
r
p
r
p
r
p
Log renin
–0.18 0.039 –0.18 0.039 0.24 0.006
0.07 0.44
Log aldosterone
0.05 0.55 0.07 0.43 0.14 0.11
0.23 0.017
Log ARR
0.17 0.052 0.18 0.034
–0.04 0.64 0.14 0.12
Whites (
n
=
179)
24-hour SBP 24-hour DBP 24-hour HR
NA:creatinine
ratio
r
p
r
p
r
p
r
p
Log renin
–0.05 0.51 –0.07 0.34 0.06 0.41 –0.06 0.44
Log aldosterone –0.05 0.53 –0.02 0.82 0.12 0.12 –0.07 0.37
Log ARR
–0.01 0.92 –0.01 0.92 0.06 0.41 –0.02 0.81
Adjusted for age,
gender and BMI
Blacks (
n
=
127)
24-h SBP 24-h DBP 24-h HR
NA:creatinine
ratio
r
p
r
p
r
p
r
p
Log renin
–0.23 0.011 –0.25 0.005 0.26 0.004
0.08 0.42
Log aldosterone –0.04 0.64 –0.02 0.82 0.1
4
0.13
0.22 0.022
Log ARR
0.12 0.18 0.16 0.084 –0.06 0.50 0.14 0.15
Whites (
n
=
179)
24-h SBP 24-h DBP 24-h HR
NA:creatinine
ratio
r
p
r
p
r
p
r
p
Log renin
–0.15 0.042
–0.15 0.034 0.07 0.37 0.09 0.23
Log aldosterone –0.08 0.27 –0.03 0.70 0.10 0.21 –0.04 0.093
Log ARR
0.03 0.65 0.09 0.24 0.04 0.61 –0.11 0.17
SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure, HR, heart rate; NA,
noradrenaline; ARR, aldosterone-to-renin ratio; BMI, body mass index. Bold
text indicates
p
<
0.05.
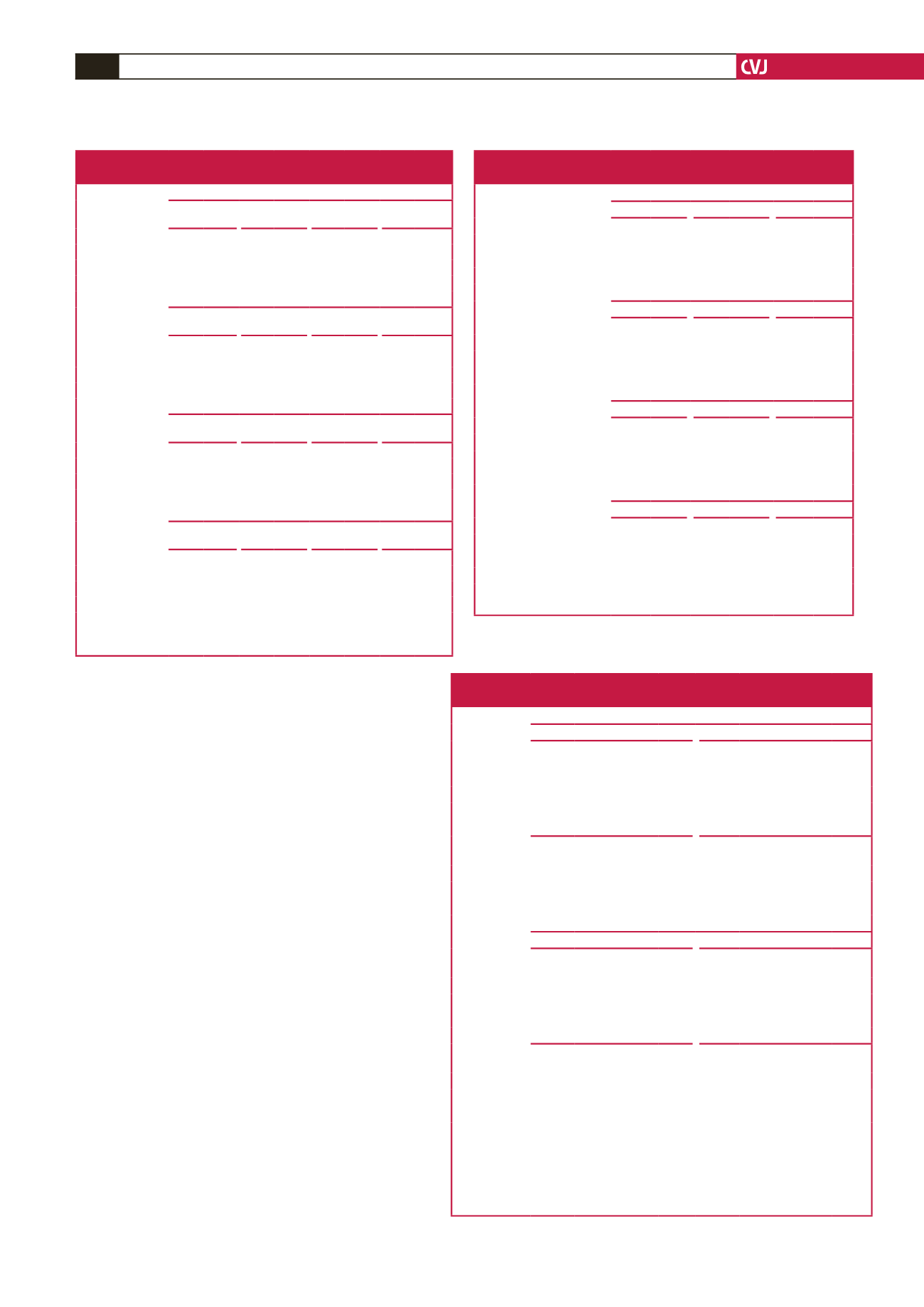
Table 4. Independent associations of 24-hour HR, night-time dipping in HR and
BP with renin, aldosterone and ARR in black and white groups
Blacks (
n
=
127)
24-h HR
% HR
Adjusted
R
2
β
(95% CI)
p
-value
Adjusted
R
2
β
(95% CI)
p
-value
Log renin
0.15 0.20 (0.93; 12.1)
0.024
0.19
–
–
Log aldosterone 0.13 0.09 (–2.12; 6.66) 0.31 0.29 –0.18 (–7.83; –0.61)
0.024
Log ARR
0.13
–
–
0.30 –0.20 (–7.28; –0.99)
0.011
% SBP
% DBP
Adjusted
R
2
β
(95% CI)
p
-value
Adjusted
R
2
β
(95% CI)
p
-value
Log renin
0.10
–
–
0.12 0.10 (–2.91; 11.2) 0.25
Log aldosterone 0.14 0.23 (1.07; 6.73)
0.008
0.16 0.24 (2.14; 12.8)
0.007
Log ARR
0.12 0.18 (0.18; 5.23)
0.038
0.12 0.15 (0.83; 8.95)
0.11
Whites (
n
=
179)
24-h HR
% HR
Adjusted
R
2
β
(95% CI)
p
-value
Adjusted
R
2
β
(95% CI)
p
-value
Log renin
0.22
–
–
0.13 0.10 (–1.62; 9.42) 0.17
Log aldosterone 0.22
–
–
0.13
–
–
Log ARR
0.22
–
–
0.13 –0.09 (–6.63; 1.67 ) 0.24
% SBP
% DBP
Adjusted
R
2
β
(95% CI)
p
-value Adjusted
R
2
β
(95% CI)
p
-value
Log renin
0.01 0.12 (–0.54; 7.27) 0.09 0.06 0.16 (0.46; 10.3)
0.033
Log aldosterone 0.0001
–
–
0.05 0.08 (–1.36; 6.48) 0.20
Log ARR
0.0001
–
–
0.04
–
–
–, log renin, log aldosterone and log ARR did not enter the forward stepwise model. Indepen-
dent variables included in the model: age, waist-to-hip ratio, gender, gamma-glutamyltrans-
ferase, cotinine, urinary Na
+
:K
+
ratio; total cholesterol:high-density lipoprotein cholesterol
ratio, glycosylated haemoglobin, tumour necrosis factor-
α
, estimated glomerular filtration
rate and total peripheral resistance. Associations with % dipping variables were additionally
adjusted for daytime measurements. ARR, aldosterone-to-renin ratio; SBP, systolic blood
pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HR, heart rate. Values in bold indicate
p
<
0.05.